Inhaled Foreign Body
This describes a foreign object which becomes lodged in the respiratory tract.
– A foreign body can be anything which is easily inhaled, such as toys, buttons, pieces of food
– It can cause an upper airway obstruction by lodging in the trachea/larynx or obstruct deeper in a bronchus
Upper airway obstruction
This is a foreign body which obstructs the larynx or the trachea blocking airflow into the respiratory tract
– This leads to choking and it is a life-threatening emergency
Symptoms:
Signs of choking (coughing, breathlessness, loss of consciousness), cyanosis, stridor
Management:
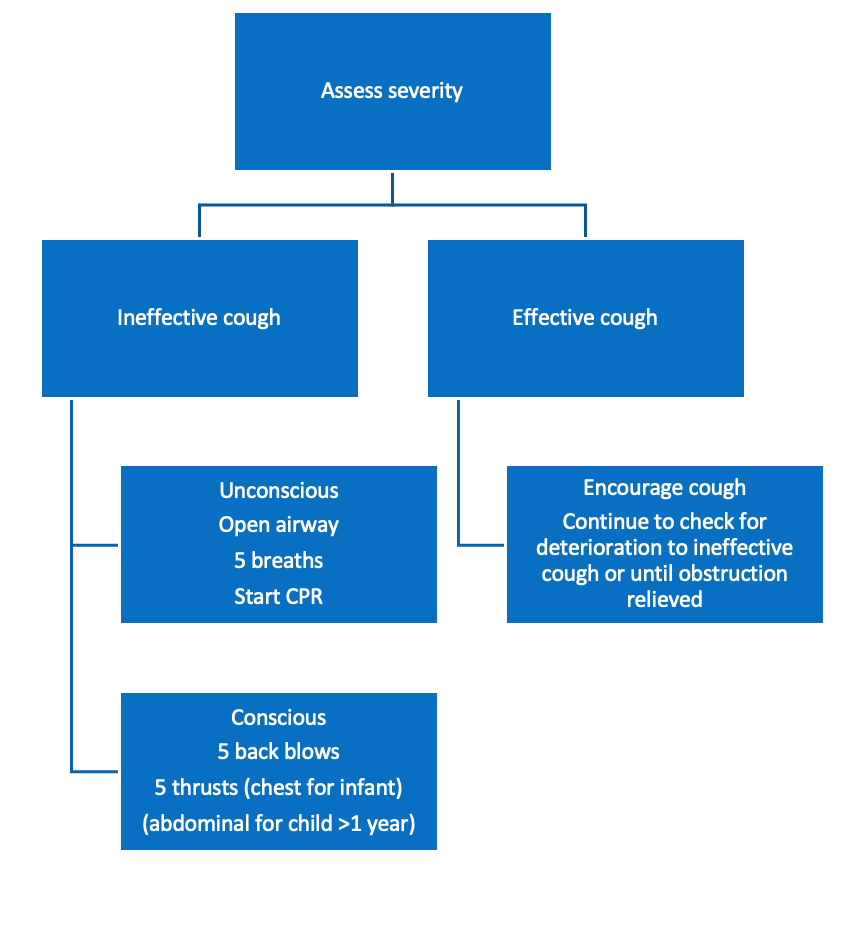
When managing choking in children, you must discern whether the cough is effective or ineffective:
Effective:
– An effective cough is a loud cough, where child can take a breath before coughing
– The child will be fully responsive and will cry or provide a verbal response to questions
Ineffective:
– An ineffective cough is one that is quiet or silent cough and will be seen in a child who is unable to breath
– The child will be unable to vocalise and will have decreasing levels of consciousness and cyanosis
Guidelines for choking:
i) If infective cough and child is unconscious:
– Open mouth + look for object –> If seen, remove with single finger sweep
– Open the airway and attempt 5 rescue breaths
– If no response, proceed immediately to CPR
ii) If ineffective cough but child is conscious:
11st give 5 back blows –> Put infants <1 year in head-downwards prone position.
– Children >1 year should be in the forward leaning position like adults
2nd give 5 thrusts –> Infants <1 receive chest thrusts with 1 finger above the xiphisternum
– For children (> 1 year), give abdominal thrusts
iii) If effective cough –> Encourage coughing and continue to check for deterioration to ineffective cough
Lower airway obstruction
This describes a foreign body lodged in main or lobar bronchus (usually right main bronchus)
– Partial obstruction –> the foreign body acts as a ball-valve, trapping air distal to the obstruction
– Complete obstruction –> results in atelectasis distal to the foreign body
Symptoms:
This can present acutely but also can go unnoticed for several days
– Abrupt onset cough in a previously well child (if acute)
– May cause signs of respiratory distress (tachypnoea, tachycardia, cyanosis)
– Unilateral expiratory wheeze
– Unilateral decreased breath sounds (complete obstruction) or hyper-resonance (partial obstruction)
Tests:
CXR shows foreign body (if radio-opaque)
Management:
ENT referral for bronchoscopy and removal of foreign body

