The liver is essential for life and carries out many important functions. It has a specialised arrangement:
– It consists of thousands of lobules giving it an organised structure
– Blood flows in through the hepatic artery and portal vein inwards towards the hepatic vein via the hepatic sinusoids
– Lining the sinusoids are hepatocytes (functional units of the liver)
– Between these are bile canaliculi, which help to drain bile outwards.
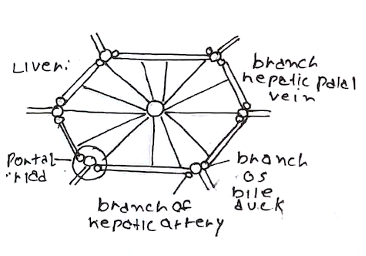
This counter current flow is helpful as it gives a sustained gradient making it easy for cells to secrete substances from the blood to the bile.
The functions of the liver can mainly be summarized into 4 types. By learning the functions in this way, it makes it much easier to then work out the symptoms of liver failure:
| Haemodynamic | Synthetic | Metabolic | Immunological |
| Controls blood pressure of the portal system | Makes clotting factors | Makes lipid soluble compounds water soluble | Makes acute phase proteins |
| Removes old blood cells | Synthesises bile | Removes toxins from blood | |
| Makes albumin | Carbohydrate/lipid metabolism |
One of the most important roles of the liver is to secrete bile which is involved in fat metabolism
– Bile is made up of cholesterol and bile salts which are secreted into the duodenum
– A key component is bilirubin, which is formed of the breakdown of haem from red blood cells.
– This passes into the gut with bile and is excreted in the faeces and the urine.
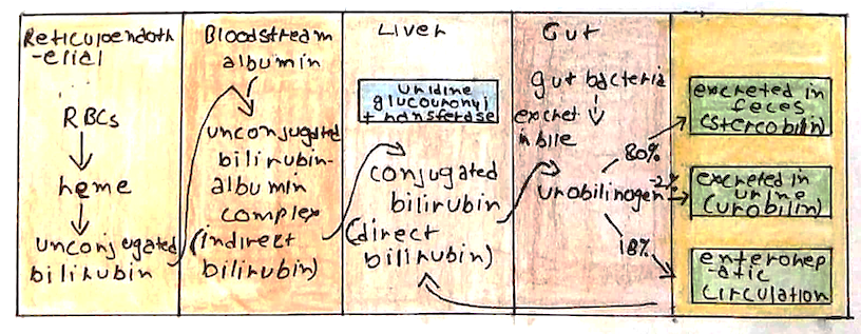
Bilirubin Lifecyle
- Haem is broken down and metabolised into unconjugated bilirubin
- This gets converted to biliverdin
- Converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase.
- In liver, bilirubin becomes conjugated by the enzyme uridine glucoronyl transferase (UGT)
- Conjugated bilirubin is excreted in the bile and further metabolized by gut bacteria
- It can then be found as stercobilin in faeces and urobilin in urine
(Some bilirubin is reabsorbed and can circulate in the enterohepatic circulation)
N.B. There is an oral naturally occurring bile acid called Ursodiol/Ursodeoxycholic acid.
– This acts to decrease liver production of bile and the reabsorption of cholesterol
– It is indicated in gallstone disease and in patients with rapid weight loss to prevent stones developing due to high cholesterol saturation of bile.
– Also used treat primary biliary cholangitis as it relieves itch and prevents further damage to hepatocytes

