This is a general term which describes a bacterial infection anywhere of the urinary tract.
It is usually caused by an infection which arises from the enteric bacteria in the gut.
It is also classified as uncomplicated (normal renal structure/function) or complicated (producing a structural/functional abnormality of urinary tract)
Risk factors
Decreased urine flow – due to dehydration, or obstructions within the urinary tract
Increased bacterial entry – due to sexual intercourse, incontinence
Higher bacterial growth – diabetes, immunosuppression, catheter use, pregnancy
Female – they have a less vertical urethra making bacterial travel easier
Key tests
Urine dipstick – positive leukocyte esterase and nitrites
Urine microscopy and culture – this is the gold standard test
Blood tests – FBC, U&E and blood cultures (to assess for bacteraemia)
Ultrasound – used in patients with upper UTI and those unresponsive to treatment.
Although we can use diagnostic tests, in non-pregnant women, if they have ≥ 3 symptoms of UTI, you can treat this empirically without the requirement of more tests.
We can divide UTI’s into upper and lower UTIs:
Cystitis (lower UTI)
This is the term which describes an infection of the bladder, usually due to bacteria.
Causes
E. coli – this is a gram negative bacteria commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract
Staphylococcus saprophyticus – this is a skin commensal bacterium which has a higher incidence in young, sexually active women
Proteus mirabilis – gives alkaline urine with ammonia smell
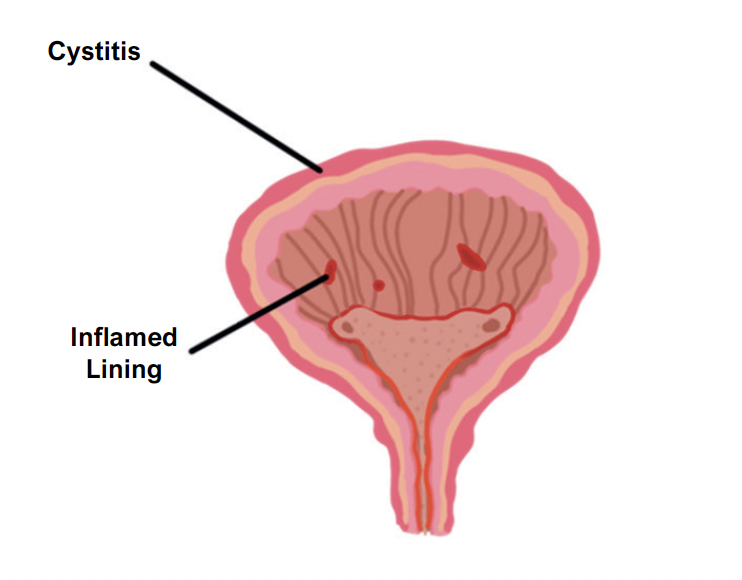
Symptoms
Triad of dysuria (pain when urinating), urinary frequency and urgency
Suprapubic pain
Can cause a pungent urine smell +/- blood in the urine
Systemic signs like fever/vomiting are usually absent
Management
Antibiotics, e.g., nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim
Acute Pyelonephritis (upper UTI)
This describes an infection of the kidney.
Like cystitis, it is usually due to an enteric infection which ascends the tract.
Therefore, a significant risk factor is vesicoureteral reflux.
Causes
E. coli (most common), Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella
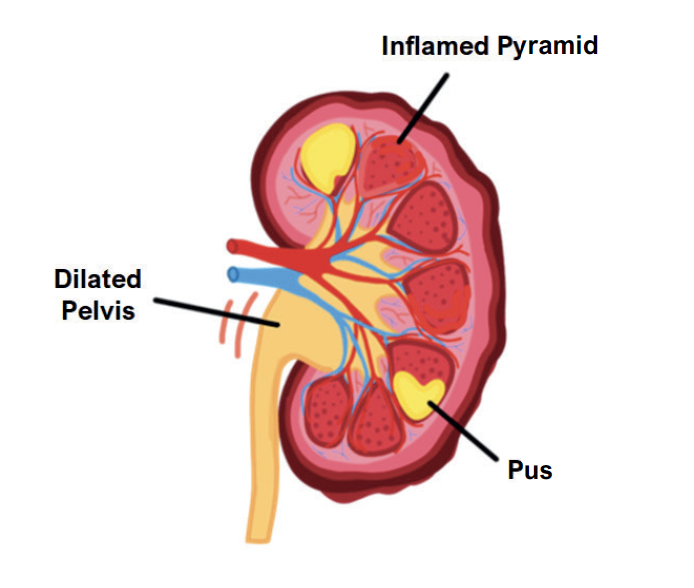
Symptoms
Triad of dysuria (pain urinating), urinary frequency and urgency
Loin pain
Can cause a pungent urine smell +/- blood in urine
Vomiting and fever
Hallmark is finding white cell casts in the urine
Management
Antibiotics according to local guidelines e.g., broad spectrum cephalosporin or quinolone (e.g., ciprofloxacin)

