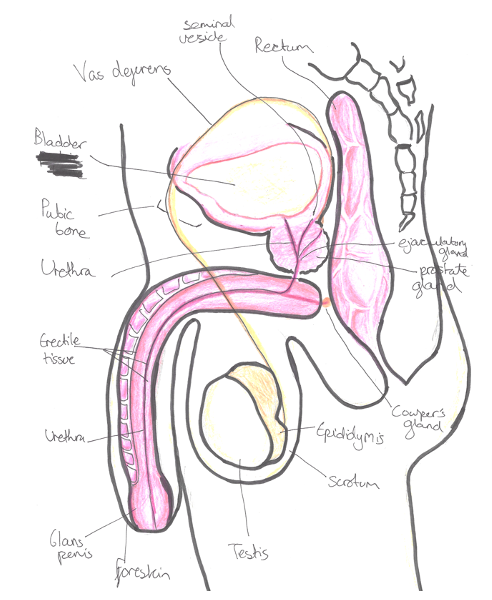
Testes
These are the main male reproductive organs which are suspended in the scrotum on the pedicles of the spermatic cords.
– These hang outside the body as the lower temperature is needed for effective spermatogenesis
– They develop from the posterior abdominal wall and carry peritoneum as they migrate through the inguinal canal.
– This peritoneum forms a double layer (tunica vaginalis) around the testes.
– The residual connection to the peritoneal cavity is obliterated as the processus vaginalis.
– Testes are also covered by outer fibrous tunica albuginea
– At the head of the testis is the epididymis, which absorbs water
Blood supply:
Gonadal artery (direct branch of abdominal aorta)
Venous drainage:
Pampiniform plexus –> gonadal veins –> IVC on right/ renal vein on left side
Nerve input:
Sympathetic effects from T10 –> pain referred to periumbilical region
Vas deferens
This enters abdominal cavity at deep inguinal ring.
– It is responsible for carrying sperm from testis to the urethra
– It unites with duct of seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory ducts. These two ducts pierce the prostate to open onto seminal colliculus into the urethra.
Blood supply:
Artery of the vas (from superior vesical artery)
Seminal vesicles
These release up to 60% of the fluid found in semen
– The excretory duct of each seminal gland unites with the vas deferens to form two ejaculatory ducts.
Prostate gland
After exiting the bladder, the urethra passes through the prostate gland.
– This produces fluid that is needed to provide nutrients for the sperm cells.
– From middle age, the prostate naturally enlarges and can start to compress the urethra.
– The prostate makes a protein called PSA, which increases as the prostate enlarges.
– Therefore, it is monitored in men as raised values can be a marker of underlying prostate cancer
Urethra
This tube connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus in the penis.
– Internal urethral sphincter at bladder neck is made of smooth muscle, which relaxes when the bladder is full. Also contracts in ejaculation to prevent retrograde ejaculation.
– External urethral sphincter is made of striated muscle giving voluntary control over urination (innervated by pudendal nerve)
– 3 parts of urethra – prostatic, membranous (narrowest part) and spongy urethra

Cremaster muscle
This is part of the spermatic cord and holds the testicles.
– It gives rise to the cremasteric reflex, important in clinical diagnoses.
– This reflex is elicited by lightly stroking the superior and medial part of the thigh
– The normal response is an immediate contraction of the cremaster muscle pulling up the ipsilateral testis
Penis
This is divided into the root, body and glans
– The body is made of two groups of erectile tissue, corpora cavernosa and a ventral corpus spongiosum which engorge in blood.
– Glans is formed by expansion of corpus spongiosum + has external urethral meatus.
– Prepuce (foreskin) is attached to the glans below by a frenulum (membrane)
– Entire body of penis is surrounded by deep fascia sleeve called Buck’s fascia.


