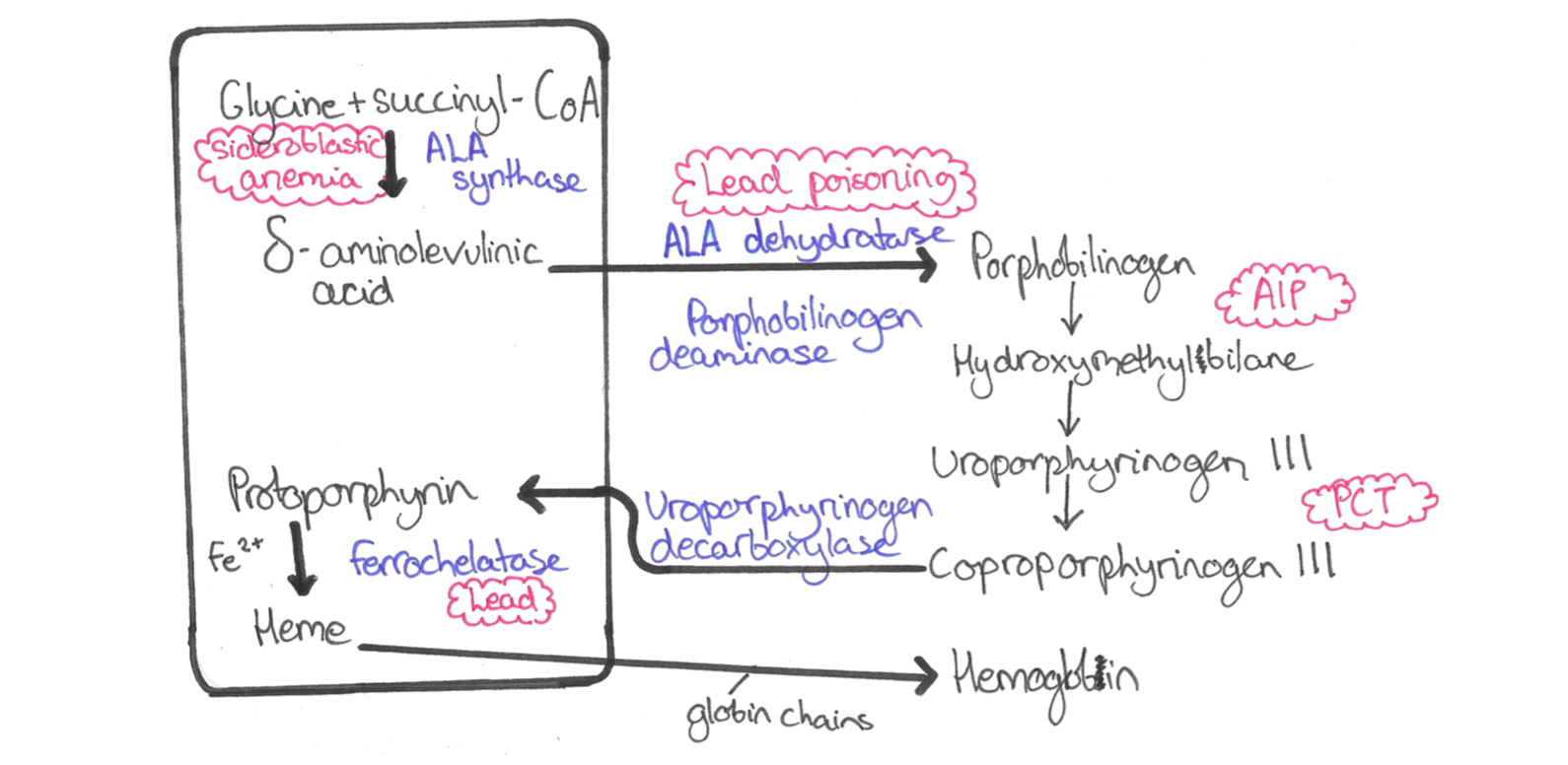
This is a group of rare disease causes by various errors of porphyrin biosynthesis, genetic or acquired.
– Porphyrin is made in a series of enzyme reactions.
– Depending on the faulty part, there is accumulation of either porphyrinogens (unstable precursors of porphyrins) or initial reactants like d-aminovulinic acid.
– The initial reactants are neurotoxic, whilst porphyrins induce photosensitivity + free radical formation.
Acute intermittent porphyria
This is an autosomal dominant condition due to a defect in porphobilinogen deaminase, which is much more common in females
– The results in the toxic accumulation of d-aminolaevulinic acid and porphobilinogen
– It characteristically presents with acute intermittent attacks from triggers, often in young women.
Triggers:
– Infection
– Surgery
– Drugs
– Cytochrome P450 enzyme inducers
Symptoms:
GI –> abdominal pain, vomiting (colic and fever)
Neuro –> Seizures and motor problems
Cardio –> Sympathetic overload gives hypertension + tachycardia
Psychiatric –> Mood disturbances (depression and anxiety)
If urine is left to stand it will turn deep red
Diagnosis:
– Urine shows raised porphobilinogen levels
– RBC enzyme essay –> shows deficiency in the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase
– Blood test shows raised serum levels of d-aminolaevulinic acid and porphobilinogen
Management:
– 1st line is IV Haematin (inhibits production of porphyrinogen precursors)
– IV fluids (correct electrolytes) + high carbohydrate diet
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
This is a liver-based porphyria which is due to a problem with uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
– This is a more chronic porphyria and does not present as acute intermittent attacks
Causes:
– Genetic defect in enzyme or due to liver damage (alcohol, hepatitis C)
Symptoms:
– Photosensitive rash on the face and hands with skin fragility and blisters.
– Excess hair growth all over body with darkening of the skin
Tests:
– Urine shows raised levels of uroporphyrinogen
– Pink fluorescence of urine under UV light using a Wood’s lamp.
Management:
– Phlebotomy (guided by serum iron levels)
– Chloroquine can be used

