Coagulation Disorders
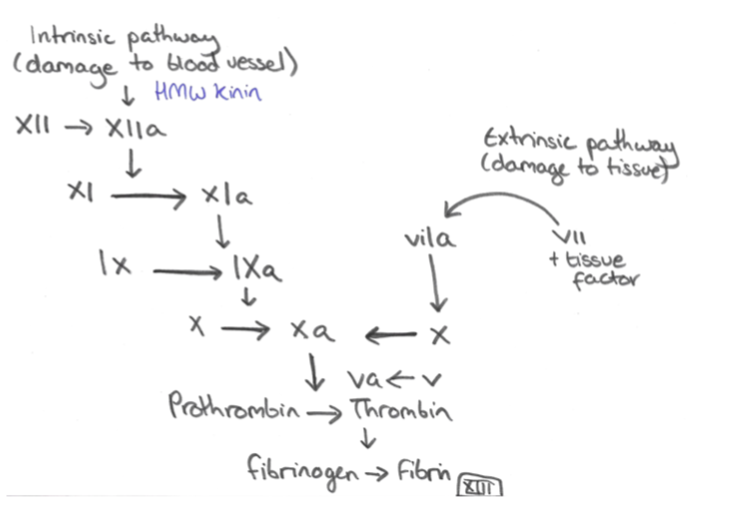
These disorders are caused by a problem relating to one or more of the factors in this coagulation cascade.
– Typically, they lead to delayed bleeding from joints and muscle and also after surgery.
Haemophilia A
This is a genetic deficiency of Factor VIII
– It is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern (mostly affects males) but also spontaneous mutation
Symptoms:
– Deep tissue, joint (haemarthroses) and prolonged post-surgical/trauma bleeding
– This can lead to haemophiliac arthropathy (resembles osteoarthritis but due to recurrent hemarthroses)
Tests:
– Raised APTT and low Factor VIII assay
– Normal PT, thrombin time and platelet count/bleeding time
– PTT corrects if you mix normal plasma with patient’s plasma
Management:
– For minor bleeds, desmopressin –> raises Factor VIII levels
– Major bleeds –> Recombinant Factor VIII (but 10% develop antibodies against factor VIII treatment)
Haemophilia B (Christmas Disease)
This is the same as Haemophilia A in all regards, except mutation is in Factor IX
Management:
Recombinant factor IX
Acquired Haemophilia (AH)
This is a rare autoimmune disorder occurring in people who do not have family history of haemorrhage
– Due to an acquired antibody against a coagulation factor (usually VIII) giving impaired function
Causes:
50% idiopathic
50% in elderly with co-existing SLE, RA, MS (other autoimmune diseases)
Symptoms:
Similar to Haemophilia A
Tests:
Raised PTT + low Factor VIII + Factor VIII autoantibody
– The raised PTT does not normalize if you mix normal plasma with patient’s plasma as you still have Factor VIII autoantibody inhibitor.
Management:
Steroids with cyclophosphamide
Vitamin K Deficiency
This is activated by epoxide reductase and is needed for the carboxylation of factors II, VII, IX and X
Causes:
– In newborns, lack of GI bacteria that make Vitamin K
– Long term antibiotic therapy kills Vitamin K producing GI bacteria
– Malabsorption of fat-soluble Vitamins
Mangement:
– Newborns –> IM Vitamin K injection given prophylactically to prevent haemorrhage
– Adults –> IV Vitamin K if emergency bleeding, use human Prothrombin Complex
Von Willebrand Disease
This is a genetic deficiency of vWF which activates the intrinsic pathway and causes platelet aggregation
– It is the most common inherited coagulation disorder with autosomal dominant inheritance
– In addition to poor platelet aggregation, vWF is needed to stabilise Factor VIII.
Symptoms:
These resemble a platelet disorder causing mucosal and superficial bleeding usually
Tests:
– Raised Bleeding time + High APTT due to decreased factor VIII
– PT is normal
– Abnormal ristocetin test – ristocetin induces platelet agglutination by causing vWF to bind platelets.
Management:
– Desmopressin –> increases vWF release from endothelial cells + stimulate Factor VIII
– If mild bleeding –> Tranexamic acid – If VIII deficient –> give Factor VIII concentrate
Haemophilia | Von Willebrand’s | Vitamin K deficiency | |
APTT | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
PT | – | – | ↑ |
Bleeding time | – | ↑ | – |
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
This is the pathological activation of the coagulation cascade, due to leakage of tissue factor into circulation.
– TF is released in response to cytokines (IL-1), TNF, endotoxins and trauma
– It leads to multiple small clots depleting the coagulation system resulting in heavy bleeding
Causes:
– Sepsis –> endotoxins from bacteria induce endothelium to make tissue factor – Malignancy – mucin activates coagulation
– Trauma
– Pregnancy – amniotic fluid leak has coagulants in it
Symptoms:
– The consumption of all clotting factors and platelets causes bleeding
– Also causes microthrombi formation giving infarction and can cause renal failure
– Fibrin strands form haemolysing passing RBCs leading to hemolytic anaemia
Tests:
– Decreased platelet count + low fibrinogen
- Increase in PT, APTT and bleeding time
- Raised D-Dimer (good screening test for DIC)
Management:
– Address the underlying cause
– Transfusion of blood products (platelets) + cryoprecipitate (contains coagulation factors)

