Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
This is an inherited autosomal dominant condition that leads to multiple hormoneproducing tumours in endocrine glands. It is divided into three types:
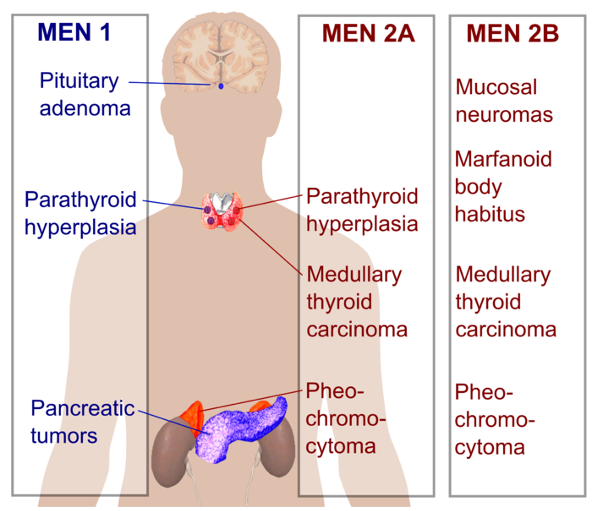
Type 1 is due to a mutation in the MEN1 tumour suppressor gene. In type 1, the most common presentation is hypercalcaemia due to parathyroid hyperplasia
Type 2 is due to a RET oncogene (receptor tyrosine kinase) mutation and is further divided into 2 types.
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia – Type 1
This is a subtype which consists of the following. 3Ps:
Parathyroid hyperplasia, without altering hormone secretion.
Pituitary prolactinoma/GH tumour – Most of these are prolactinomas, then GH secreting tumours.
Pancreas: insulinoma/gastrinoma – Can lead to Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia – Type 2a
This subtype consists of the following symptoms:
Medullary thyroid cancer
Phaeochromocytoma
Parathyroid hyperplasia
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia – Type 2b
This subtype consists of the following symptoms:
Medullary thyroid cancer
Phaeochromocytoma
Tall, thin Marfan’s body type
Dry eyes or lack of tears
Delayed puberty
It usually manifests in early childhood
Management
This involves medical management depending on the hormones affected as well as treatment of the affected glands usually by surgical excision

