There are many skin conditions which are associated with an underlying systemic pathology.
Diabetic Skin Conditions
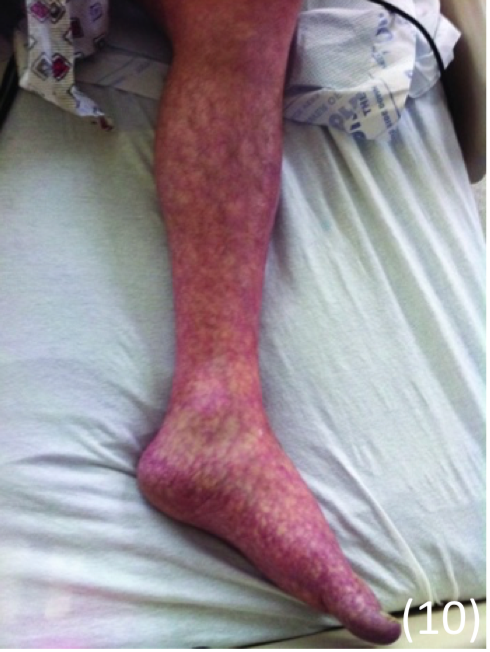
Diabetic dermopathy
This is the presence of atrophic brown patches on shins, “shin spots”
– It occurs due to changes in the microvasculature and leakage of blood into the skin – Occurs in about a third of diabetic patients
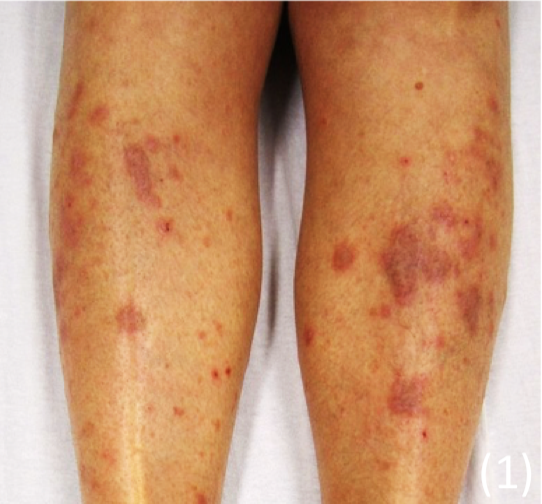
Necrobiosis Lipiodica
These are yellow/brown waxy plaques that are slow growing and can ulcerate
– They are also seen in rheumatoid arthritis
– Lesions occur usually on the patient’s shins due to collagen degeneration
– Appears as hardened, raised area of skin with yellowish tint
Treatment
– PUVA (psoralen and ultraviolet A)
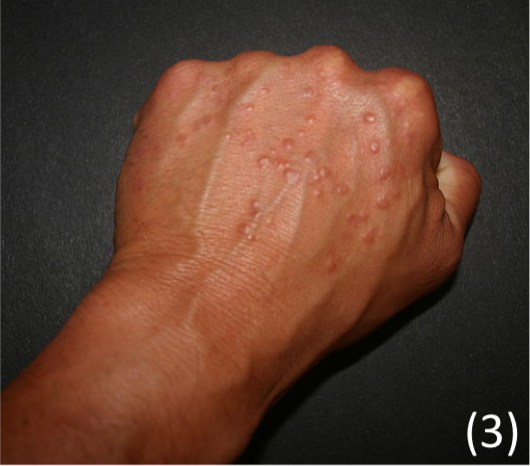
Granuloma annulare
A rare chronic skin condition that presents as reddish bumps on skin in a circle
– Occur due to clustering of T cells below the skin surrounding macrophages
– Often seen on backs of forearms, hand and feet over the joints and knuckles
– Usually asymptomatic but can burn or itch a little
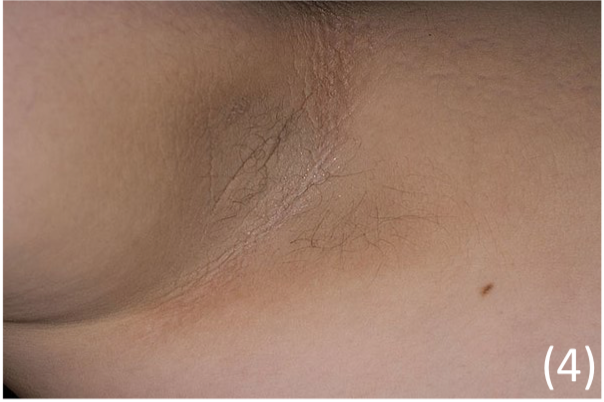
Acanthosis Nigricans
This refers to hyperplasia with darkening of the skin in the axilla, groin and neck
– It is a non-specific skin sign which is associated with a host of systemic conditions:
– Diabetes Mellitus
– Obesity
– Oral contraceptive pill
– Hypothyroidism
– GI cancer
Diabetic ulcers
This is a painless neuropathic ulcer which occurs due to peripheral neuropathy.
– Patients lose sensation which causes overpressure on pressure points on the feet leading to microtrauma and tissue breakdown
– Poor wound healing means the tissue is not repaired causing ulcer formation
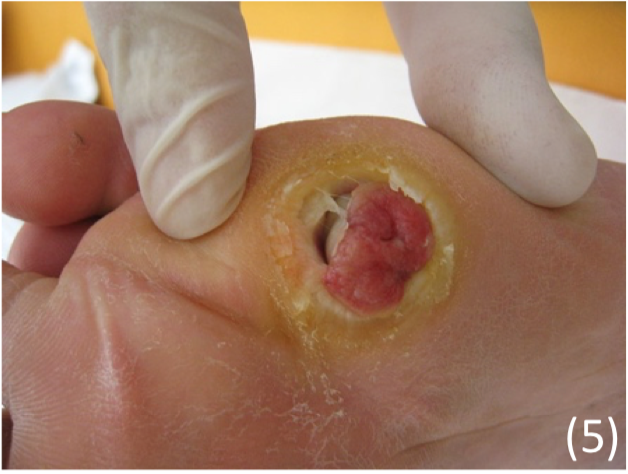
Appearance
– Seen on the soles of the feet as penetrating ulcer on toes
– Seen with trophic changes (shiny skin, hair loss) + reduced sensation
Management
– Refer to diabetic foot centre + specialised cushioned footwear
Chronic Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
This is an autoimmune skin condition associated with coeliac disease, which occurs when IgA antibodies become deposited in the skin.
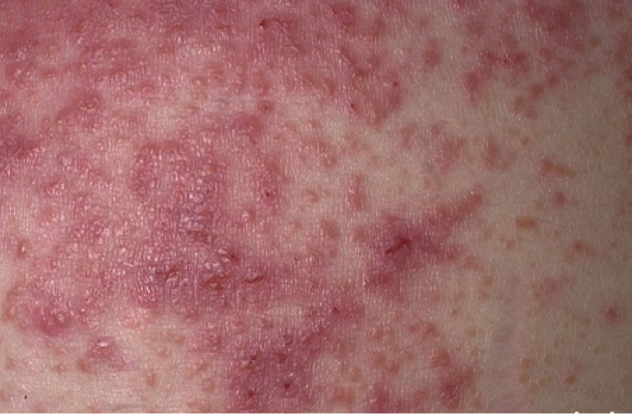
Appearance
– Symmetrical itchy vesicular lesions on the skin which appear in groups
– The blisters often become eroded and crusted due to the itching
– Classically seen on extensor surfaces like the elbows, knees and buttocks
Diagnosis
– Immunofluorescence of skin biopsy shows deposition of IgA in dermis
Management
– Gluten-free diet
– Dapsone –> antibiotic which inhibits synthesis of dihydrofolic acid, reduces itch in 3 days
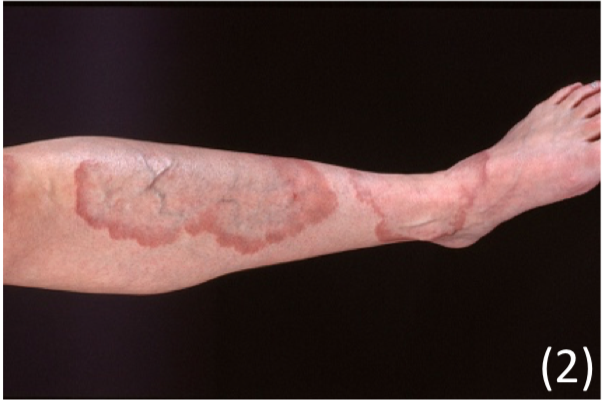
Pyoderma gangrenosum
This is a painful ulcer that occurs on the lower limbs suddenly at site of minor injury
– Not caused by a pathogen, but instead by improper functioning of neutrophils
– Usually idiopathic but associated with chronic inflammatory disorders
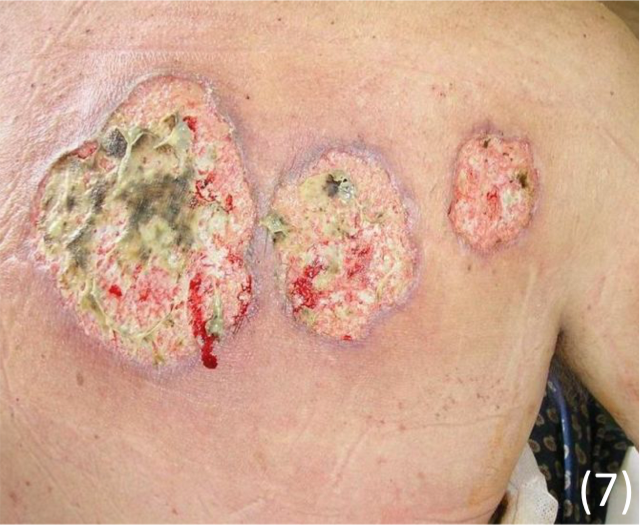
Appearance
– Starts as a small red pustule/bump but then the skin breaks down quickly
– This eventually leaves a deep ulcer with a purplish border
– If left untreated, the ulcer may keep growing larger, persist or slowly heal
Associations:
– Inflammatory bowel disease
– Rheumatoid arthritis, SLE
– Lymphoma, myeloid leukaemia – Primary biliary cirrhosis
Management:
– 1st line is oral steroids
– Large ulcers need oral steroids, ciclosporin or biological agents
Erythema Nodosum
An inflammatory disorder which affects the subcutaneous fat cells under the skin
– This leads to the development of painful red nodules usually on the shins
– It is more common in women than men usually seen in ages from 20-40.
– The lesions do not form ulcers and heal without scarring
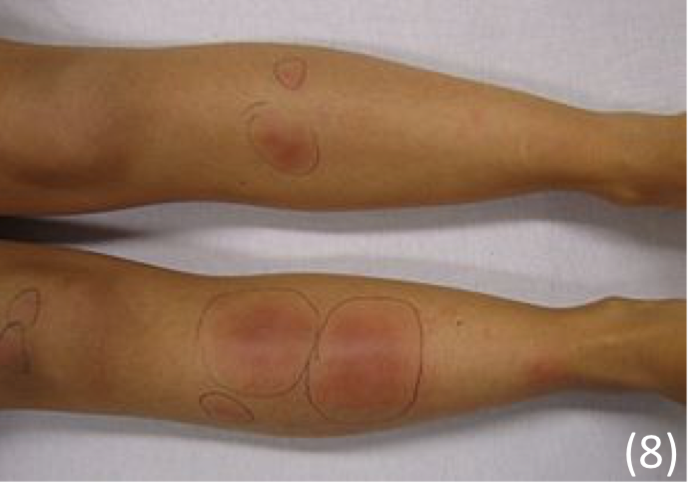
Appearance
– Erythematous tender plaques mainly on shins + thighs
– Initially red, but then go purple, brown or like a bruise before resolving themselves
Associations:
– Chest infection –> TB, streptococci
– Sarcoidosis
– Inflammatory bowel disease
– Drugs –> Amoxicillin, contraceptive pill
– Lymphoma
– Pregnancy
SLE Skin Conditions
This is a type 3 hypersensitivity reaction where immune system dysregulation leads to immune complex formation and deposition within many organs. A common place of deposition to occur is the skin giving classic signs:
Alopecia
This is an autoimmune condition causing distinct patches of hair loss
Discoid lupus
Inflammatory condition consisting of scarring, annular scaly plaques on exposed parts of face/scalp
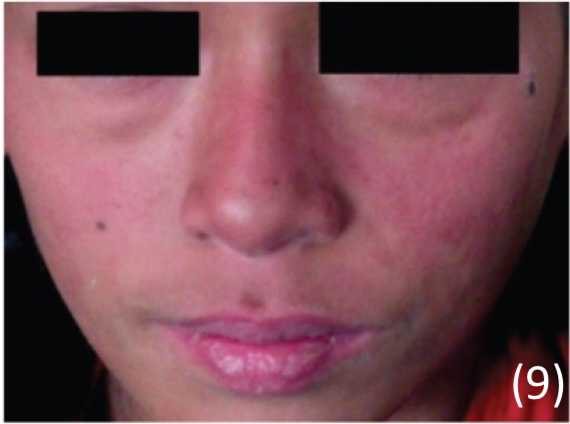
Photosensitive rash
This is a red rash, occurring across the cheeks and bridge of nose
– Can be a very mild red blush, blotchy or can be flat or raised
– Classically there is nasolabial sparing which gives the classic butterfly distribution
Livedo Reticularis
A skin condition due to swelling of venules caused by capillary obstruction by small clots
– Looks like a lacey purplish discolouration of the skin following a vascular pattern
– Due to conditions which increase the risk of forming clots in small vessels, e.g. SLE, polyarteritis nodosa