Viruses are composed of a genome (nucleic acid) with a protein shell (capsid). This is sometimes surrounded by a phospholipid membrane called an envelope.
– The most important part of the life cycle is being able to replicate the viral DNA within host cells.
DNA viruses
These use a host DNA-dependent RNA polymerase to make mRNA
– The mRNA is translated in cytoplasm and used to make protein components
– These protein components are put together in the cytoplasm to make new virus particles which can be released from the cell.
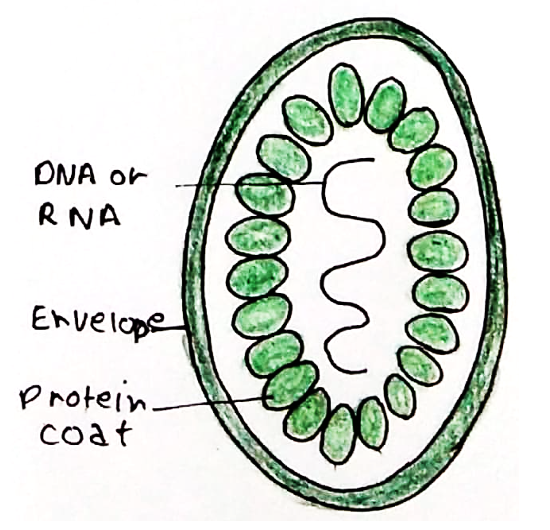
RNA viruses
These can be subdivided according to whether they are double or single stranded as well as their replication strategies:
i) Double stranded:
These must be transcribed into mRNA by a virus encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
ii) Single stranded:
These are further subdivided into positive sense, negative sense and retroviruses. Each has a slightly different replication strategy.
–> Positive sense:
This means the RNA strand acts as mRNA and can be directly translated
– This is then used to make RNA dependent RNA polymerase, which can replicate the genome
–> Negative sense
This is first transcribed into mRNA by viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase which is packaged inside the virus particle
– This generates a positive sense mRNA strand which can then be translated to make proteins
–> Retrovirus:
This is a type of +ve strand RNA virus.
– However, the RNA is first made into a DNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase enzyme and integrated into the host cell genome, before using the replication strategy of DNA viruses
Immunity
Immunity to viruses is mediated by both the innate and adaptive immune system:
Innate:
This uses phagocytes and natural killer cells to phagocytose virus-infected cells
– Infected cells undergo apoptosis to prevent viral replication
– Interferon release –> these are chemicals which induce the activation of an anti-viral state.
Type | IFN | Function | Medical use | Side effects |
| I | IFNα | Made by WBCs – induces antiviral state | Hepatitis B and C Kaposi sarcoma | Flu-like symptoms Depression |
| II | IFNß | Made by fibroblasts – induces antiviral state | Reduces frequency of exacerbations in Multiple Sclerosis | |
| III | IFNγ | Made by NK and T cells – promotes inflammation and up-regulates macrophages | Chronic granulomatous disease |
Adaptive:
This uses CD8+ cytotoxic T cells which phagocytose infected cells
– Also, antibodies neutralise virus particles alone or in combination with complement.
Vaccination
A key aspect of immunity for viruses is vaccination, which can exist in 3 main types:
i) Live attenuated
These are naturally produced or lab modified strains of pathogen with reduced virulence
– These induce both cellular and humoral immunity and give immunity which is long lived
– However, virus can revert to virulence and cause problems in immunocompromised patients
ii) Inactivated
These are chemically treated to kill organism, much safer as they are not infectious
– However, need multiple injections as not long lasting and usually only induce antibody immunity
iii) Component
These are elements of the organism to allow immunogenicity, often used with adjuvants
| Live Attenuated | Inactivated | Toxoid | Subunit/conjugate |
| Yellow Fever | Hepatitis A | Diphtheria | Hepatitis B |
| MMR: Measles, Mumps, Rubella | Rabies | Pertussis | Human Papilloma Virus |
| Polio (Sabin) | Polio (Salk) | Tetanus | Meningococcus (bacteria) |
| Varicella-Zoster | Influenza | Pneumococcus, haemophilus |

