A hernia is the abnormal protrusion of tissue through an opening, which can occur in many different locations.
They usually present as a visible lump, with an expansible cough impulse
Risk factors
These increase intra-abdominal pressure or weaken the abdominal wall
Heavy lifting
Previous abdominal surgery
Constipation
Obesity
Symptoms
Visible lump, with expansible cough impulse
They are usually soft, painless, and reducible
Complications
Irreducibility/incarceration – this means the contents cannot be pushed back into their original position
Obstruction – this refers to hernia containing bowel; the contents are compressed so the bowel lumen is not patent resulting in bowel obstruction
Strangulation – this is when the compression stops the blood supply to the bowel resulting in ischaemia, necrosis and pain. It is a surgical emergency.
Key tests
1st choice imaging is ultrasound. CT scanning is used if diagnostic unclear
Management
If asymptomatic, conservative management, e.g., advise weight loss and monitoring
If there are complications (e.g., severe pain, strangulation), surgery is required.
Elective surgery for hernias includes herniorrhaphy, the removal of the hernia sac (putting it back in place) and strengthening of wall muscles
Hernioplasty refers to herniorrhaphy with the addition of a foreign material (e.g., mesh) to strengthen the wall
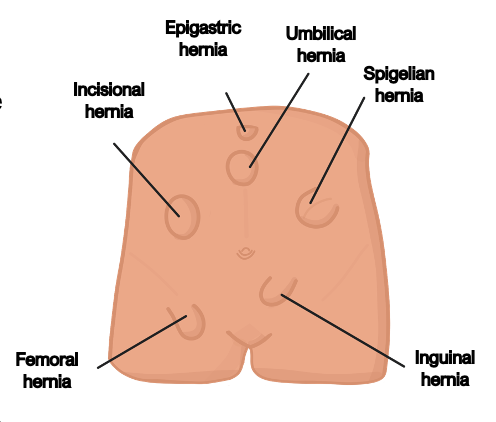
Specific Hernias
Inguinal Hernia
This is most common hernia for both sexes (but more commonly seen in men than women) and is divided into two types. It presents as a painless groin swelling.
To distinguish between the two, try to reduce the hernia and occlude the deep ring.
Ask the patient to cough. If the hernia remains restrained then it is indirect, otherwise it is a direct inguinal hernia.
Indirect
This is where abdominal tissue enters the deep inguinal ring and can pass out the superficial ring.
This is lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels and can extend down into the scrotum.
The hernias can enter scrotum producing a lump which does not transilluminate.
You cannot “get above” the swelling (cannot palpate the superior surface).
Direct
This is a hernia where abdominal tissue pushes through a defect/weakening in the posterior wall of the inguinal canal, called Hasselbach’s triangle.
It is less common than an indirect inguinal hernia and medial to inferior epigastric vessels.
Femoral Hernia
This refers to the protrusion or bulge or abdominal tissue below the inguinal ligament, through the femoral canal, presenting as a groin mass.
It occurs more commonly in post-menopausal women, and it is lateral and inferior to the pubic tubercle, but overall, it is still less common than inguinal hernias.
Unlike the inguinal hernias, it is more likely to be irreducible and strangulate.
Good, bad and the ugly
Spigelian Hernia
This occurs through the linea semilunaris in the lateral edge of the rectus sheath
It is below and lateral to the umbilicus
Richter’s hernia
This is a rare but dangerous type of hernia
It is when only the antimesenteric side of the bowel wall herniates, not whole lumen
Can result in strangulation and necrosis without signs of obstruction
Maydl hernia
This involves herniating double loop of bowel – strangulated portion can stay in abdomen

