Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) (von Recklinghausen disease)
This is a complex multi-system disorder, caused by loss of protein Neurofibromin needed in many cells
– An autosomal dominant condition which is caused by a mutation/deletion of NF-1 gene on Chromosome 17

Skin features:
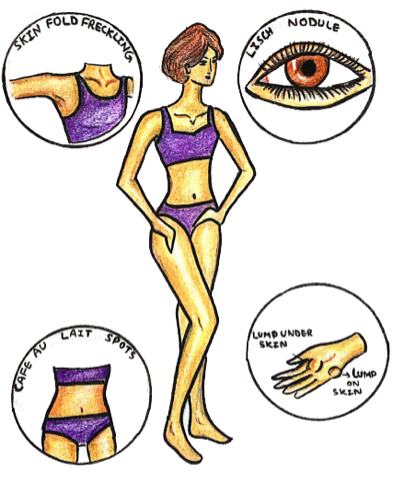
>5 Café au lait marks >1.5cm diameter (uniformly pigmented brown macules)
– Due to a collection of pigment producing melanocytes in the epidermis of the skin
– Freckles found in the axilla and groin region
– Peripheral neurofibromas
Other Organs:
– Spine –> Scoliosis
– Eye –> Lisch nodules (dome shaped gelatinous masses on iris surface)
– Endocrine –> Pheochromocytoma (adrenaline secreting tumour of the chromaffin cells)
Associations:
– Can lead to learning disabilities
– Hypertension – due to renal artery stenosis + phaeochromocytoma
– Tumours – Neurofibromas + Optic nerve gliomas
Neurofibromatosis Type 2
This is an autosomal dominant condition which is due to a genetic mutation on Chromosome 22.
Symptoms
– Gives bilateral acoustic neuromas –> sensorineural hearing loss + tinnitus and vertigo
– Tumours are benign but can cause problems due to compression and raised ICP
– Also gives multiple intracranial tumours such as schwannomas and meningiomas
Management
– Hearing tests annually after puberty for affected families + MRI scan
– Neurosurgery for acoustic neuromas –> can gives hearing loss and facial palsy
Tuberous Sclerosis
A rare neurocutaneous disorder that causes benign tumours to grow in the brain and other organs like heart, skin
– Due to autosomal dominant mutation in TSC1 (chromosome 9) or TSC2 (Chr 16) leading to hamartoma formation
Skin features:
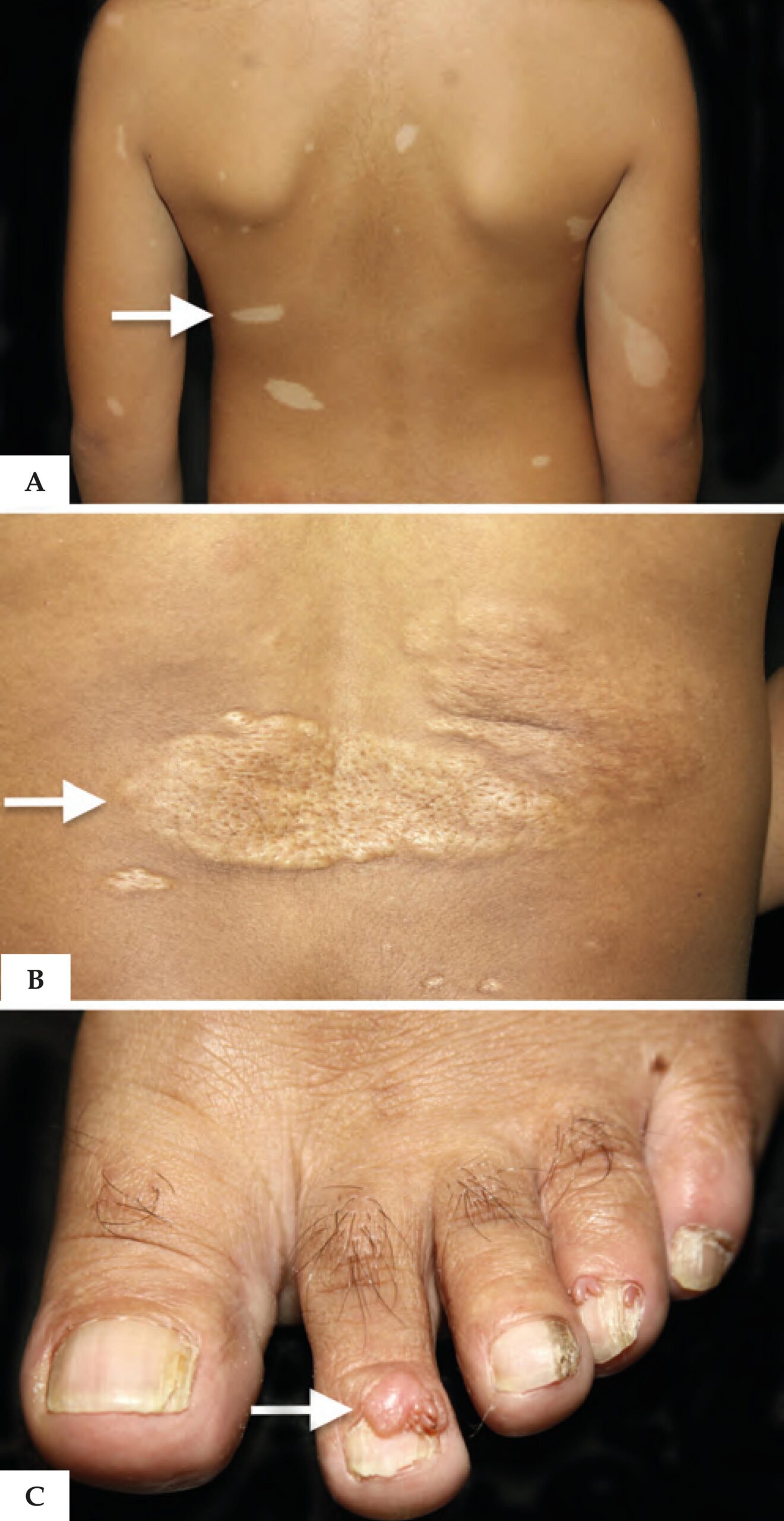
– Hypopigmented “ash-leaf spots” which fluoresce under UV light
– Angiofibroma in butterfly pattern around nose (adenoma sebaceum)
– Connective tissue naevus (Shagreen patch) – elevated patch of skin on back
– Subungual fibromata (under nails)
Other Organs:
– Heart –> Rhabdomyonas (benign tumours of muscle) of the heart
– Lung –> multiple lung cysts
– Kidneys –> Polycystic kidney disease + benign tumours
– Eye –> haemartoma formation on the retina giving visual distrubances
– CNS –> epilepsy due to harmatoma formation in central nervous system
Associations:
– Associated with developmental delay